Basic principle of Moving magnet type velocity Transducer
When a permanent magnet moves inside a coil, the change in the length of the air gap varies the reluctance. Hence the output voltage is directly proportional to the rate of change of the length of the air gap (change in length produced by velocity). Thus the output voltage becomes a measure of the velocity when calibrated.
Description of Moving magnet type velocity Transducer
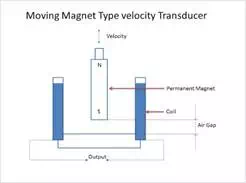
The sensing element which is a rod is a permanent magnet.
1. The rod is rigidly coupled to the device whose velocity is being measured.
2. There is a coil surrounding the permanent magnet.
3. The permanent magnet is movable, that is, it can move in and out of the coil.
Operation of Moving magnet type velocity Transducer
1. The instrument is fixed to the device whose velocity is to measured.
2. Due to the application of the velocity, the permanent magnet moves in or out of the coil. Due to its motion, the length of the air gap varies.
3. The output voltage also varies due to the motion of the magnet and the amplitude of the voltage is directly proportional to velocity.
4. The polarity of the output voltages determines the direction of the velocity.
Advantages of Moving magnet type velocity Transducer
1. Its maintenance is negligible.
2. The output voltage is linearly proportional to velocity.
3. Cost of manufacture is less.
Disadvantages of Moving magnet type velocity Transducer
1. Performance is affected by stray magnetic fields and hence noise is caused.
2. Frequency response is poor.
Application
Used as a velocity transducer to convert velocity to measureable voltage.



Comments are closed.