The main aim of a measuring system is to present the data in an understandable manner to the user / observer. The data presentation device is called as an output device or terminating device.
The D’Arsonval movement is a current sensing mechanism which is used in DC Ammeter, ohmmeter and Voltmeter.
Principle of D’Arsonval Movement
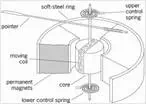
When an electric current is passed through a coil placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force. This force causes a torque in the coil that is fixed to a spindle. The spindle can rotate in fixed bearings.
The rotation of the spindle is proportional to the electric current passed through the coil. This torque that is produced is balanced after a movement against the restoring torques of springs. The torque that is produced that tends to rotate the spindle is termed as D’Arsonval Movement.
Description of D’Arsonval Movement
1. The arrangement consists of a coil which is wound over an iron core (spindle).
2. This spindle is placed between the two poles of a horseshoe magnet.
3. The spindle is attached at its end to bearings. Spiral and torsional springs are provided for restoration of the system when the extraction is removed.
4. A pointer is attached to the spindle that can sweep over the calibrated scale.
Operation of D’Arsonval Movement
1. When a current is passed through the coil, it produces a force. Due to this force, a torque is produced in the spindle which rotates it.
2. When the spindle rotates, it moves a pointer making it sweep over the calibrated scale.
3. The spring produce a restoring torque. When this restoring torque becomes equal to the excitation torque, the pointer comes to rest.
4. The rotational movement of the spindle is proportional to the supply (D.C) Current.



Comments are closed.