An Operational Amplifier, or op-amp is a voltage amplifying device designed to be used with external feedback components such as resistors and capacitors between its output and input terminals. It is a high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and usually a single-ended output. Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices.
However, an op-amp is just one type of differential amplifier. Other include,
· A fully differential amplifier which is like an op-amp, but with two outputs.
· The instrumentation amplifier which is usually built from three op-amps,
· The isolation amplifier which is like an instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp
· A negative-feedback amplifier which is usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network.
Op-amp operation
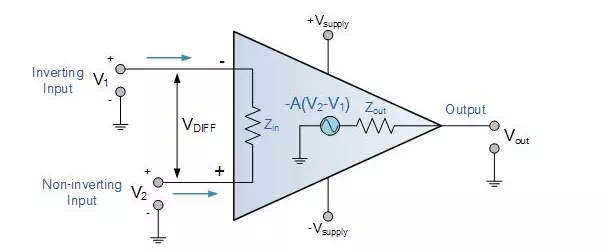
The amplifier’s differential inputs consist of a non-inverting input with voltage (V+) and an inverting input with voltage (V−). Ideally, an op-amp amplifies only the difference in voltage between the two, also called differential input voltage. The output voltage of the op-amp Vout is given by the equation,
Vout = AOL (V+ – V–)
where AOL is the open-loop gain of the amplifier. In a linear operational amplifier, the output signal is the amplification factor, known as the amplifiers gain (A) multiplied by the value of the input signal.
| Op-amp parameters· Open-loop gain is the gain without positive or negative feedback. Ideally, the gain should be infinite, but typical real values range from about 20,000 to 200,000 ohms.· Input impedance is the ratio of input voltage to input current. It is assumed to be infinite to prevent any current flowing from the source to amplifiers.· The output impedance of the ideal operational amplifier is assumed to be zero. This impedance is in series with the load, thereby increasing the output available for the load.· Bandwidth of an ideal operational amplifier is infinite and can amplify any frequency signal from DC to the highest AC frequencies. However, typical bandwidth is limited by the Gain-Bandwidth product. GB product is equal to the frequency where the amplifiers gain becomes unity.· The ideal output of an amplifier is zero when the voltage difference between the inverting and the non-inverting inputs is zero. Real world amplifiers do exhibit a small output offset voltage. |
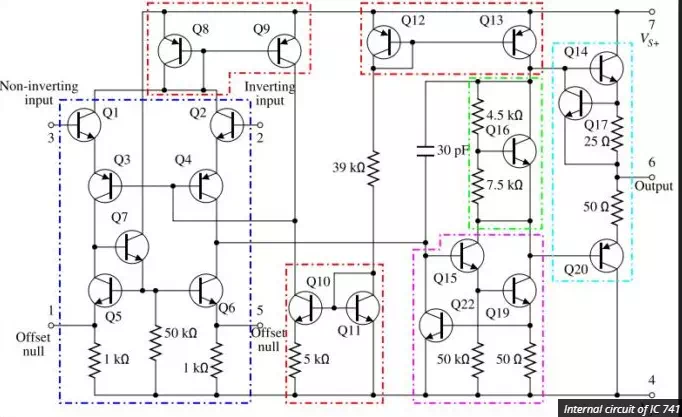
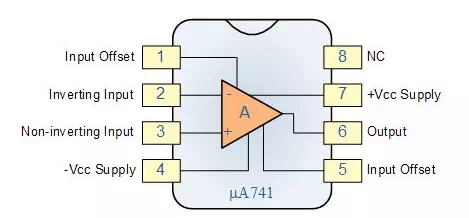
An op-amp only responds to the difference of the two voltages irrespective of the individual values at the inputs. External resistors or capacitors are often connected to the op-amp in many ways to form basic circuits including Inverting, Non-Inverting, Voltage Follower, Summing, Differential, Integrator and Differentiator type amplifiers. Op-amp is easily available in IC packaging, the most common os whom is the μA-741.