Common Source JFET Amplifier uses junction field effect transistors as its main active device offering high input impedance characteristics
Transistor amplifier circuits such as the common emitter amplifier are made using Bipolar Transistors, but small signal amplifiers can also be made using Field Effect Transistors. These devices have the advantage over bipolar transistors of having an extremely high input impedance along with a low noise output making them ideal for use in amplifier circuits that have very small input signals. The design of an amplifier circuit based around a junction field effect transistor or “JFET”, (N-channel FET for this tutorial) or even a metal oxide silicon FET or “MOSFET” is exactly the same principle as that for the bipolar transistor circuit used for a Class A amplifier circuit we looked at in the previous tutorial. Firstly, a suitable quiescent point or “Q-point” needs to be found for the correct biasing of the JFET amplifier circuit with single amplifier configurations of Common-source (CS), Common-drain (CD) or Source-follower (SF) and the Common-gate (CG) available for most FET devices. These three JFET amplifier configurations correspond to the common-emitter, emitter-follower and the common-base configurations using bipolar transistors. In this tutorial about FET amplifiers we will look at the popular Common Source JFET Amplifier as this is the most widely used JFET amplifier design.
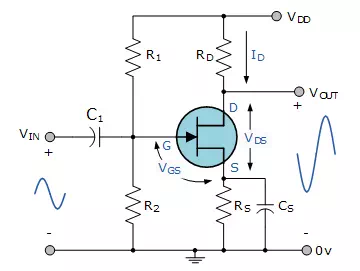
Consider the Common Source JFET Amplifier circuit configuration below.