A Bipolar Junction Transistor is a three terminals active semiconductor device formed by two back-to-back p-n junctions. The three terminals are labeled base, emitter and collector. Its main function is the current amplification between the collector or emitter currents and the base current.
There are 2 types of Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), the NPN and the PNP.
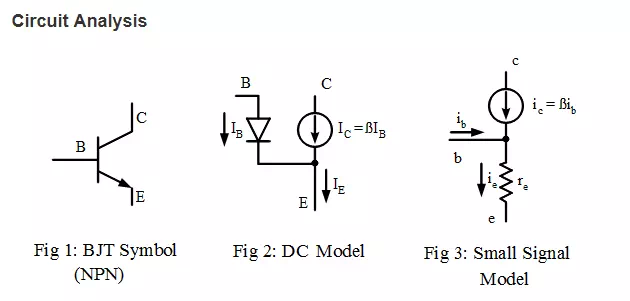
To analyse a transistor circuit,
- Do a DC analysis by redrawing the schematic
- replace the BJT symbol with its DC model.
- open circuit any capacitor and short circuit any inductor.
- If an AC analysis is required, redraw the schematic
- by replacing the BJT symbol with the small signal model.
- calculate re using IE from the DC analysis and vT=26 mV.
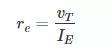
1.
- note that the AC analysis is only valid for vbe < vT
- short circuit any capacitor and open circuit any inductor. Short Circuit any DC power supply.
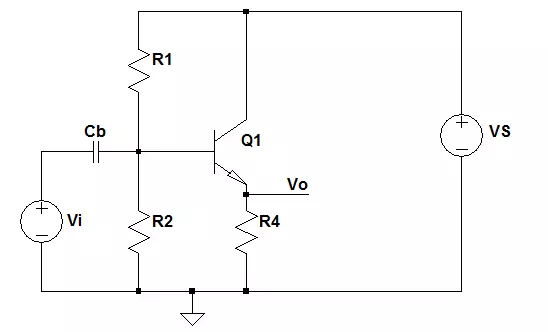
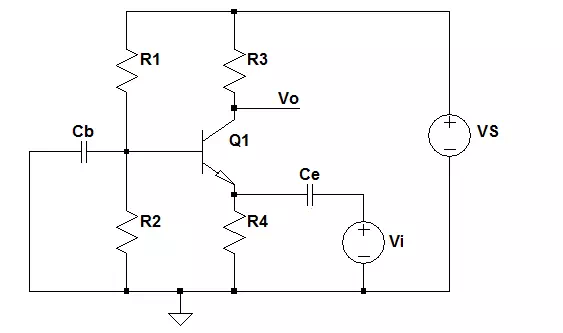
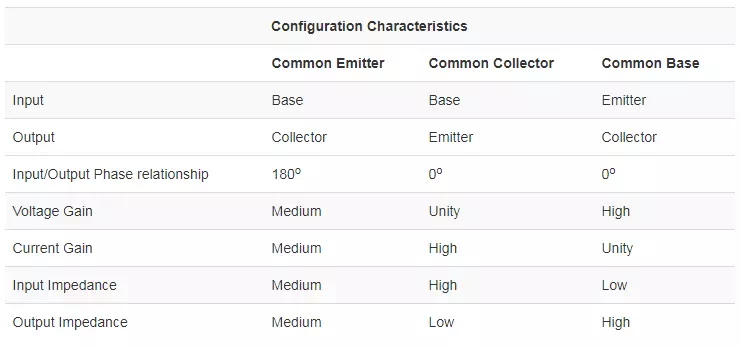
Single BJT Circuit Configuration
There are 3 configurations for the circuits with a single Bipolar Junction Transistor. They are the common emitter, common base and common collector circuits.