A truth table is a handy little logical device that shows up not only in mathematics, but also in Computer Science and Philosophy, making it an awesome interdisciplinary tool. The notation may vary depending on what discipline you’re working in, but the basic concepts are the same. This primer will equip you with the knowledge you need to understand symbolic logic. We’ll start with defining the common operators and in the next post I’ll show you how to dissect a more complicated logic statement.
Unary Operators
Unary operators are the simplest operations because they can be applied to a single True or False value.
Identity
The identity is our trivial case. It states that True is True and False is False.
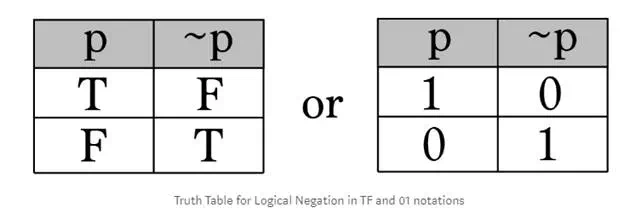
Negation
The negation operator is commonly represented by a tilde (~) or ¬ symbol. It negates, or switches, something’s truth value.We can show this relationship in a truth table. A truth table is a way of organizing information to list out all possible scenarios. We title the first column p for proposition. In the second column we apply the operator to p, in this case it’s ~p (read: not p). So as you can see if our premise begins as True and we negate it, we obtain False, and vice versa.